Establishing Fodder Beat
Fodder beet sowing checklist

The key to a successful crop is following best
practice throughout the process from paddock
selection to transition and feeding. This
information is a guide. Seek specific advice.
Open Information Sheet
Paddock selection

Industry regulations and guidelines mean many
physical features need to be considered in
selecting paddocks for grazing fodder beet. A
specific wintering plan is now required for all
winter crops, including an animal wellness plan.
Open Information Sheet
Soil fertility – fodder beet
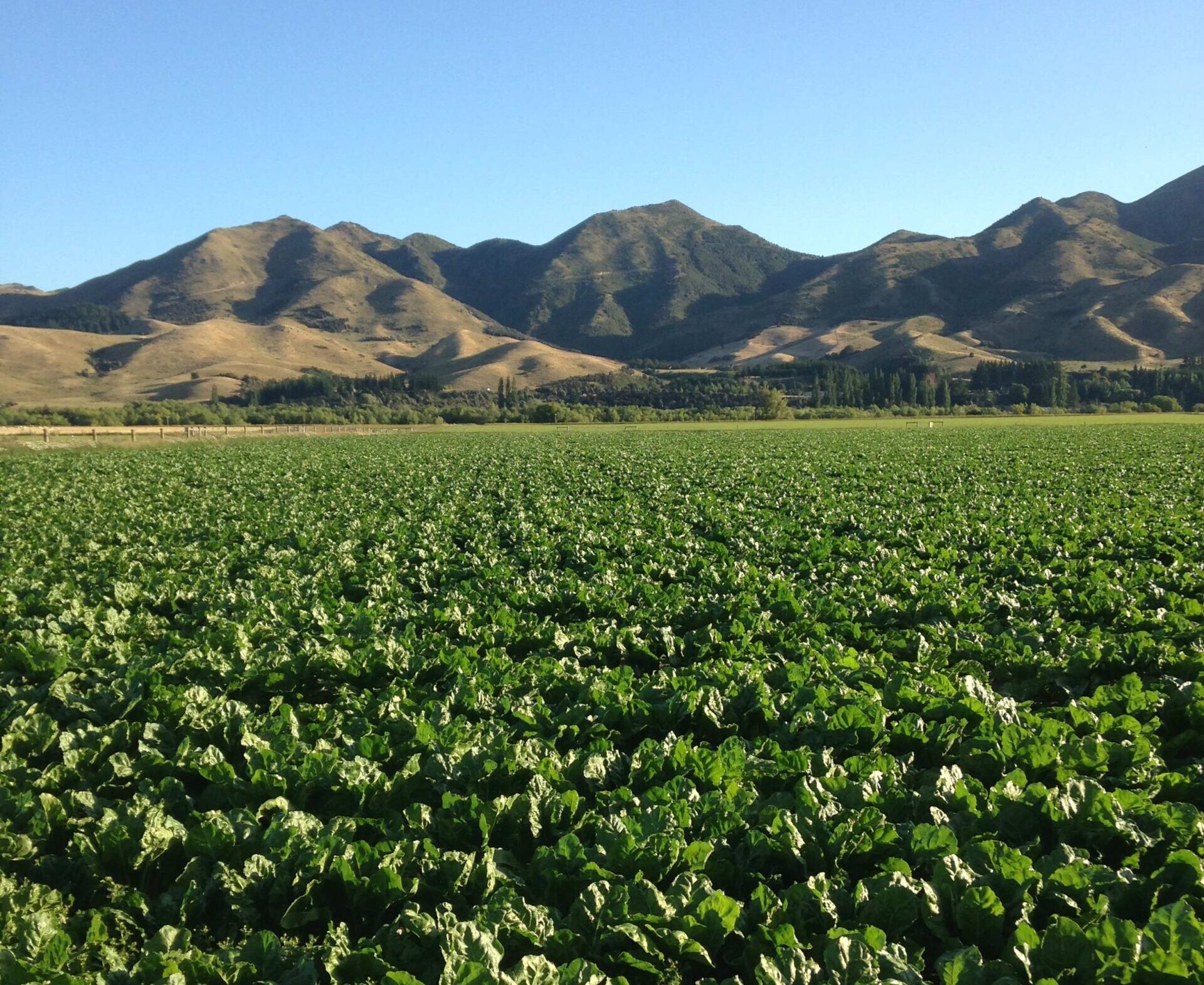

Fodder beet requires certain nutrient levels to yield well. Soil test paddock(s) 6-12 months before planting to allow time for pH or nutrient issues to be addressed. Apply and incorporate all base fertiliser before planting.
Open Information Sheet
Establishment techniques – Fodder beet
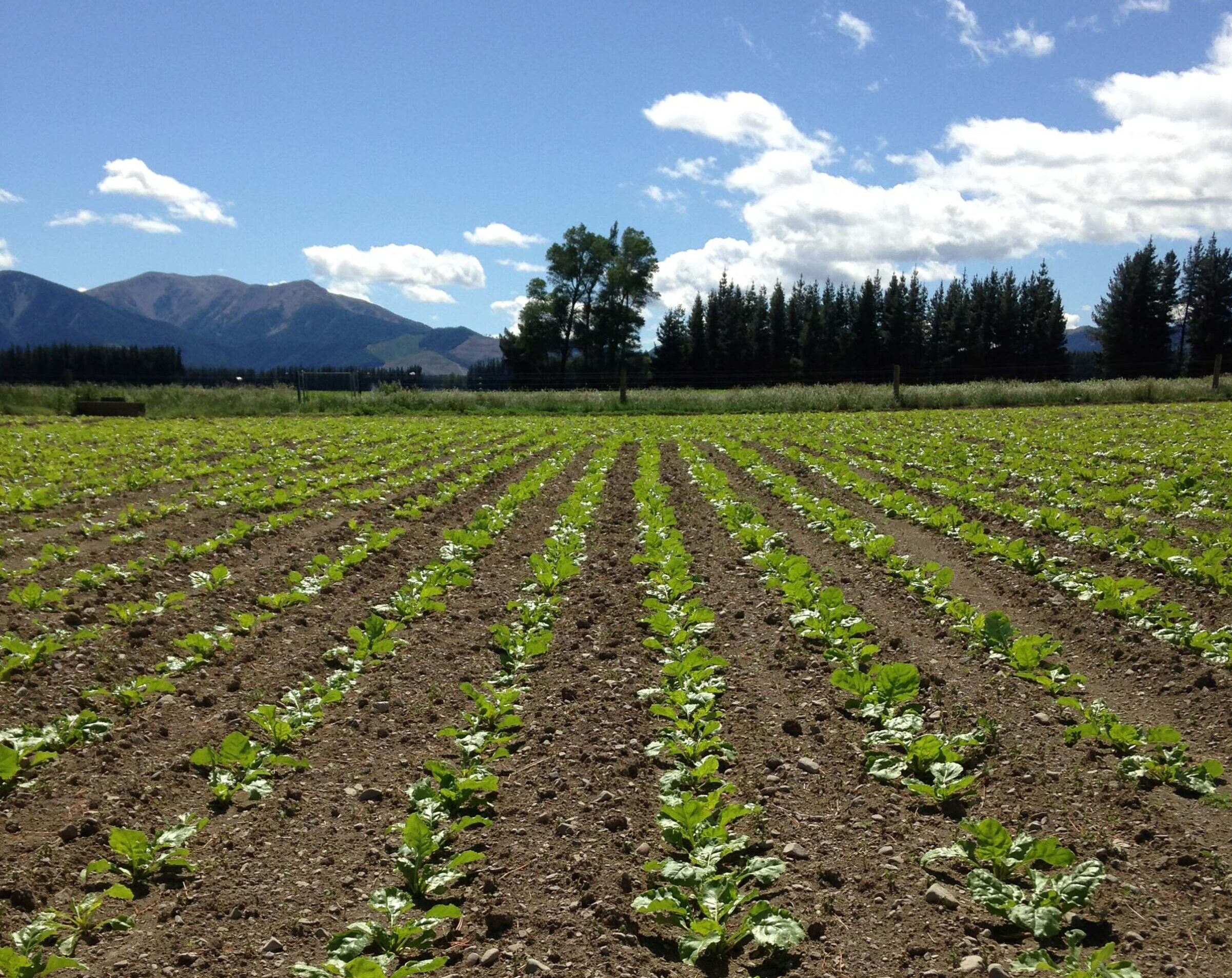

Fodder beet is a specialist crop, more intensive and expensive to grow than other forage crops. It can produce high DM yields, but these vary widely. With good management and moisture fodder beet can produce 30 t DM/ha. Typical yields are 18-24 t DM/ha.
Open Information Sheet
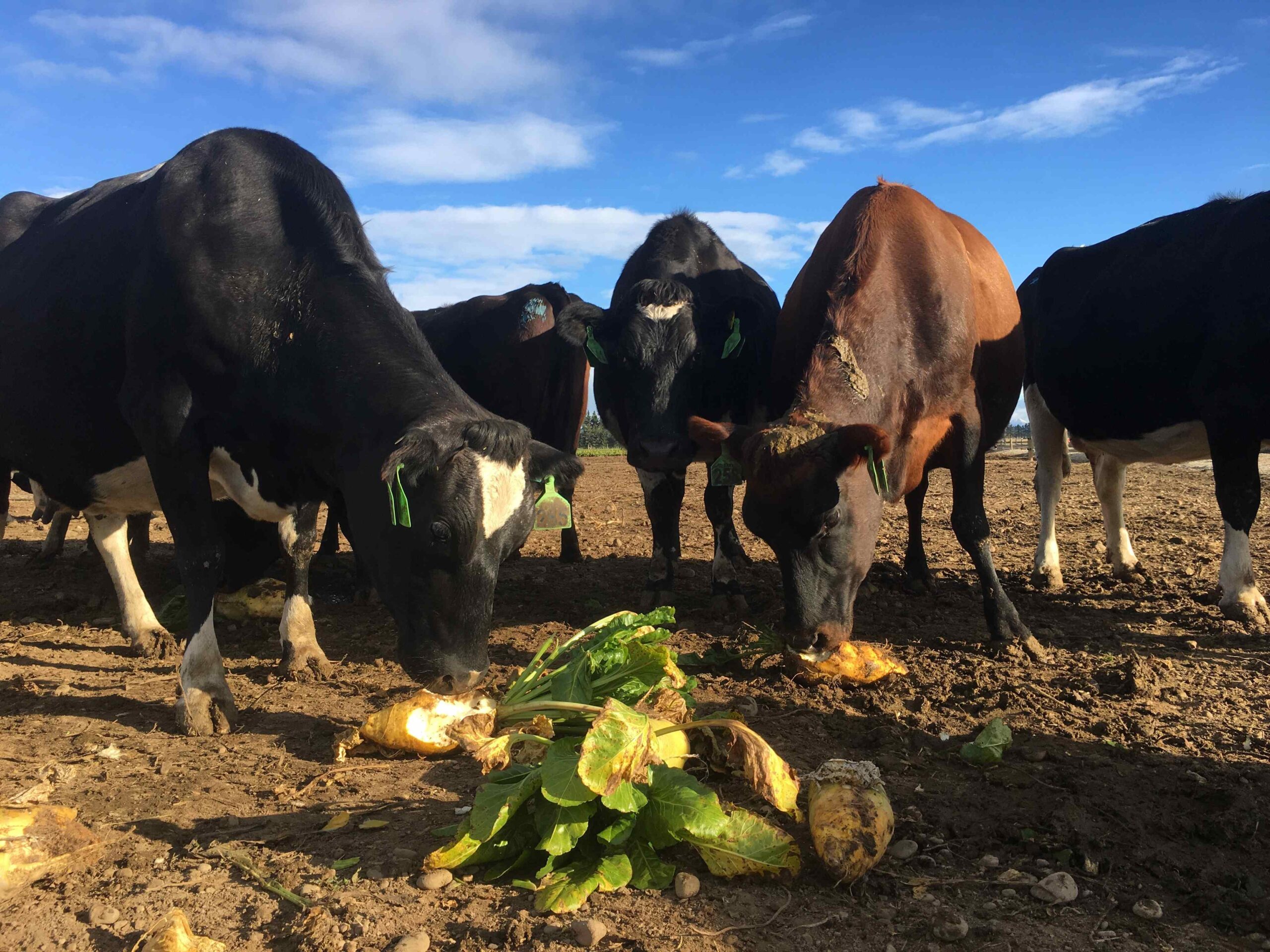
Environmental considerations

Fodder beet can have both positive and negative
impacts on the environment, and these need to be
weighed carefully depending on your farm system.
Research into environmental outcomes is still
evolving.
Open Information Sheet